Proud of our Publication in BMJ: Predicting communities with high tuberculosis case-finding efficiency to optimise resource allocation in Pakistan
- Caroline Van Cauwelaert
- Mar 31
- 3 min read
The recent publication in BMJ Public Health titled "Predicting communities with high tuberculosis case-finding efficiency to optimise resource allocation in Pakistan: comparing the performance of a negative binomial spatial lag model with a Bayesian machine-learning model" represents a significant advancement in the application of predictive modeling for tuberculosis (TB) intervention planning. As EPCON, we are proud to have contributed our Bayesian machine learning (BML) expertise to this important research.
The Challenge Addressed
Despite progress in tuberculosis treatment coverage in Pakistan, an estimated 183,000 people with TB may have gone undiagnosed in 2022. This highlights the critical need for effective models that can guide active case finding (ACF) efforts toward populations with a high probability of having undetected TB. Resource optimization is essential, as ACF activities are resource-intensive and must be strategically deployed to maximize impact.
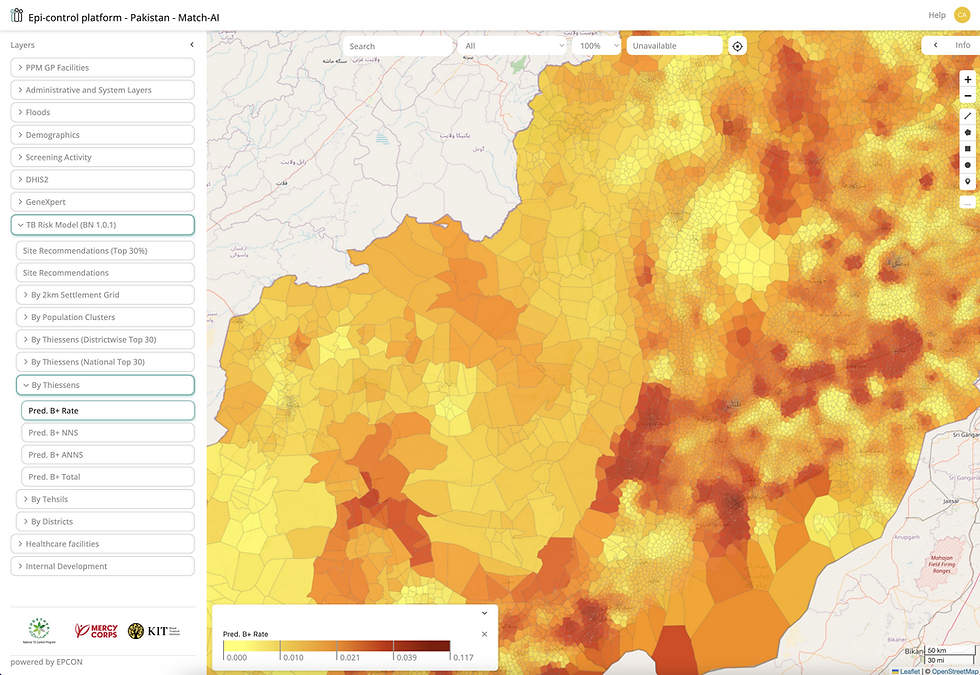
EPCON's Bayesian Machine Learning Contribution
Our team at EPCON, represented by Andreas Werle van der Merwe, Matthys Potgieter, and Vincent Meurrens, developed the Bayesian machine learning model that served as the reference model in this cross-validation study.
Our BML approach:
Employed a directed Bayesian network to represent the interactions of various covariates related to TB risk factors
Constructed the network by mining Bayesian structures from the data using mutual information and a minimum description length criterion
Utilized belief propagation for efficient inference of probability distributions for the outcome variable
Enabled the model to update beliefs about TB diagnoses when new data from chest camp events or other covariates were introduced
Provided predictions with 95% credible intervals for each prediction
Research Methodology and Findings
The study conducted a retrospective analysis of cross-sectional data collected during 510 TB chest camps conducted between September 2020 and January 2022 across 15 districts in Punjab and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa provinces in Pakistan. The research team identified 407 bacteriologically confirmed TB cases (1.9%) among 21,227 visitors screened during 414 ACF events.
Our BML model was compared with a negative binomial regression (NBR) model with spatial lag to determine which approach provided better predictive accuracy for TB hotspot identification. Key findings include:
Both models demonstrated similar predictive accuracy at the tehsil (sub-district) level
Our BML model achieved a slightly lower root mean squared error (1.02 vs. 1.03)
The predictions from both modeling approaches were remarkably similar, suggesting that predictions are more driven by covariates rather than the specific modeling framework.
Implications and Value of EPCON's Contribution
The research demonstrates that our Bayesian machine learning approach provides a robust framework for predicting TB hotspots with high case-finding efficiency. The agreement between our BML model and the NBR model increases confidence in the potential utility of these models to spatially target ACF activities in high-need, low-access areas.
As EPCON, we are particularly proud that our sophisticated Bayesian network approach performed well in this real-world application. The study validates our methodology and demonstrates that our BML approach can effectively support public health decision-making by:
Providing a practical level of discrimination when prioritizing locations for TB interventions
Enabling more efficient resource allocation for TB case finding
Supporting evidence-based decision-making in public health planning
Offering a framework that can potentially be adapted to other public health challenges
Conclusion
This research represents an important validation of EPCON's Bayesian machine learning approach in addressing critical public health challenges. The study demonstrates that our BML model provides valuable predictive capabilities for optimizing TB case-finding efforts, ultimately contributing to more effective TB control strategies in resource-limited settings.
We are proud to have collaborated with international partners including KIT Royal Tropical Institute, University of Amsterdam, Mercy Corps Pakistan, and Pakistan's National TB Program on this important work. This publication highlights EPCON's commitment to developing innovative technological solutions that can make a meaningful impact on global health challenges.


